An optical module is a photoelectric device that converts optical signals into electrical signals. It is mainly used in optical fiber communication systems for high-speed data transmission between network devices (such as switches, routers, servers, etc.). Optical modules achieve long-distance data transmission by converting electrical signals into optical signals, and restore optical signals to electrical signals at the receiving end. Optical modules are one of the core components in optical fiber communication systems.
Basic components of optical modules
An optical module usually consists of the following main components:
- Laser : Converts electrical signals into optical signals and sends them.
- Detector (Photodetector) : Receives light signals and converts them into electrical signals.
- Driver Circuitry : Controls the output of the laser.
- Modulation circuit : Modulates electrical signals so that they can be sent via optical signals.
- Fiber optic interface : usually different types of interfaces such as LC, SC, MTP, etc., used to connect optical fibers.
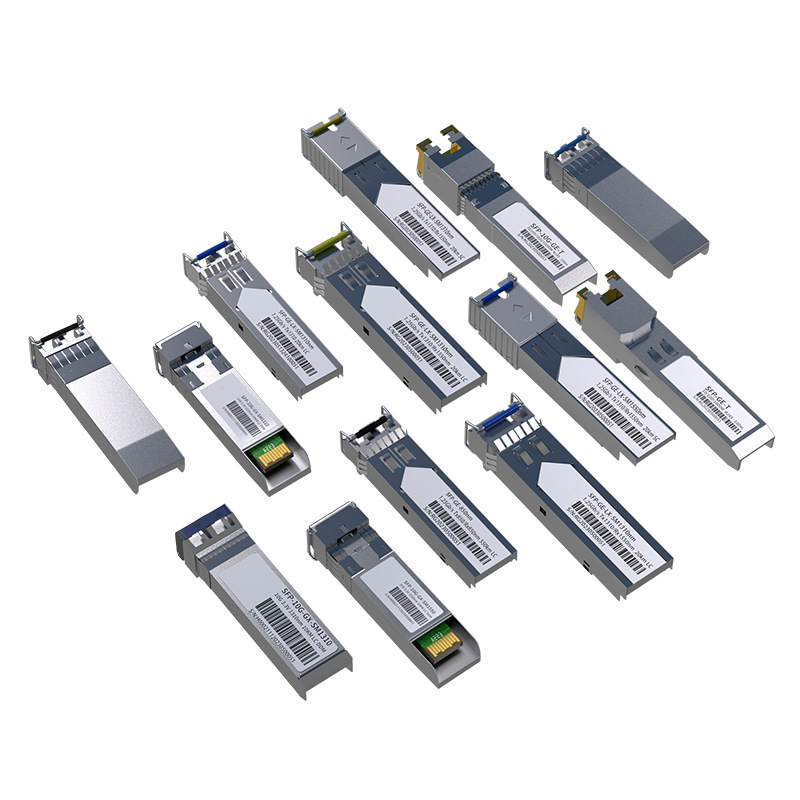

Classification of optical modules
Optical modules can be divided into many types according to different application requirements and specifications. The following are common classifications:
- Classification by speed
- 1G optical module (SFP) : supports 1Gbps transmission rate and is commonly used in Gigabit Ethernet.
- 10G optical module (SFP+) : supports 10Gbps rate and is widely used in data centers, enterprise networks, etc.
- 25G optical module (SFP28) : supports 25Gbps transmission rate and is commonly used in next-generation data center networks.
- 40G optical module (QSFP+) : supports 40Gbps rate and is suitable for networks with high bandwidth requirements.
- 100G optical module (QSFP28) : supports 100Gbps rate and is the current mainstream high-bandwidth optical module type.
- 200G and 400G optical modules : suitable for hyperscale data centers and core networks, able to meet higher bandwidth requirements.
- Classification by transmission distance
- Short Range Optical Module (SR) : Suitable for short-distance transmission, usually used in data centers, with a transmission distance of tens to hundreds of meters.
- Medium and long distance optical module (LR, Long Range) : Suitable for medium and long distance transmission, the transmission distance can reach 10 kilometers or longer.
- Ultra-long-distance optical module (ER, Extended Range) : can support transmission distances of tens or even hundreds of kilometers, and is suitable for metropolitan area networks and long-distance backbone networks.
- Classification by fiber type
- Single-mode optical module : uses single-mode optical fiber, has a longer transmission distance, and is suitable for long-distance communication.
- Multimode Optical Module : It uses multimode optical fiber and has a shorter transmission distance. It is usually used for short-distance connections within local area networks and data centers.
- Classification by interface type
- SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) : A commonly used interface for 1G and 10G rates.
- QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) : supports 40G and 100G rates.
- CFP (C Form-factor Pluggable) : Mostly used for 100G and above rates, suitable for long-distance transmission.
- OSFP and QSFP-DD : New interfaces designed for 400G networks.
Application fields of optical modules
Optical modules are widely used in the following fields:
- Data center : Enable high-speed connections between servers, storage devices, and switches.
- Telecommunications network : used for core network transmission of long-distance backbone networks and metropolitan area networks.
- Enterprise network : used for LAN connection within the enterprise.
- Other fields : such as the financial industry and the medical industry, which require a high-reliability and high-bandwidth network environment.
The standardized design and diverse transmission capabilities of optical modules make them an indispensable key component in modern fiber-optic communications.